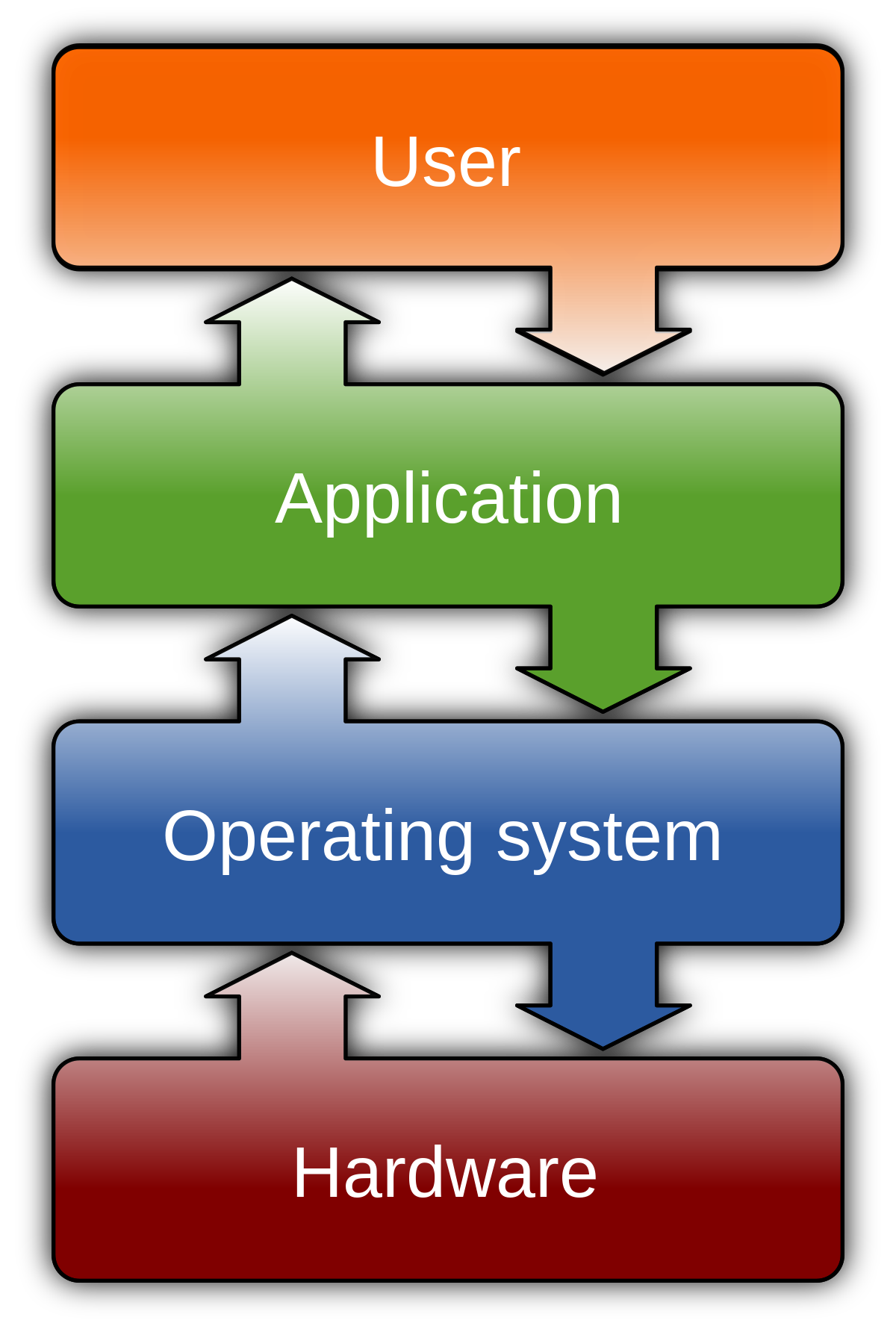
Imagine a world without computers. A world where technology doesn’t exist, and every task is done manually. It’s almost unfathomable, isn’t it? Computers have become an integral part of our lives, revolutionizing the way we work, communicate, and even entertain ourselves. But have you ever wondered what makes these machines function? What lies at the heart of every computer, silently running in the background, making everything possible? It’s the software. Yes, the software is the unsung hero, the invisible force that brings life to these machines. Whether it’s the operating system that allows you to navigate through your computer or the applications that handle your daily tasks, software is undeniably the most important component of any computer.

This image is property of www.techyv.com.
Operating System
Definition and Purpose
The operating system (OS) is a critical piece of software that serves as the backbone of a computer. It acts as an intermediary between the hardware components of a computer and the user, enabling them to interact with the computer and perform various tasks. The primary purpose of an operating system is to manage and oversee the hardware and software resources of a computer system, ensuring that they work together efficiently and effectively.
Examples of Popular Operating Systems
There are several popular operating systems available today, each offering its unique features and functionalities. Some of the most widely used operating systems include:
-
Microsoft Windows: Developed by Microsoft, Windows is the most popular operating system globally. It provides a user-friendly interface, extensive software compatibility, and a wide range of features for both personal and professional use.
-
macOS: Developed by Apple Inc. exclusively for Apple computers, macOS offers a seamless and intuitive user experience. It is renowned for its sleek design, excellent performance, and integration with other Apple devices.
-
Linux: Linux is an open-source operating system that has gained popularity for its stability, security, and flexibility. It powers a vast range of devices, including servers, smartphones, and embedded systems, and offers various distributions such as Ubuntu, Fedora, and CentOS.
-
Android: Android is a mobile operating system developed by Google, primarily designed for smartphones and tablets. It boasts a vast app ecosystem, customization options, and seamless integration with Google services.
Key Functions of an Operating System
The operating system performs a multitude of essential functions to ensure the smooth operation of a computer system. Some key functions of an operating system include:
-
Process Management: The OS manages running processes, allocating system resources such as CPU time and memory to ensure efficient multitasking and process execution.
-
Memory Management: It oversees the allocation and deallocation of memory, ensuring that each running program has sufficient memory to execute without conflicts.
-
File System Management: The OS manages access to files and directories, ensuring data storage, retrieval, and organization. It also handles file permissions, security, and backup processes.
-
Device Management: The operating system interacts with hardware devices such as printers, scanners, and network adapters, enabling communication and coordination between the devices and software applications.
-
User Interface: The OS provides a user-friendly interface that allows users to interact with the computer system easily. This interface may be a graphical user interface (GUI) or a command-line interface (CLI).
Impact on Computer Performance
The choice of operating system can significantly impact the performance of a computer. Factors such as stability, efficiency, resource management, and compatibility can all affect how well a computer functions. A well-designed operating system can optimize the use of hardware resources, enhance system responsiveness, and provide a seamless user experience. Additionally, regular updates and security patches from the operating system vendor can help protect against vulnerabilities and ensure a secure computing environment.
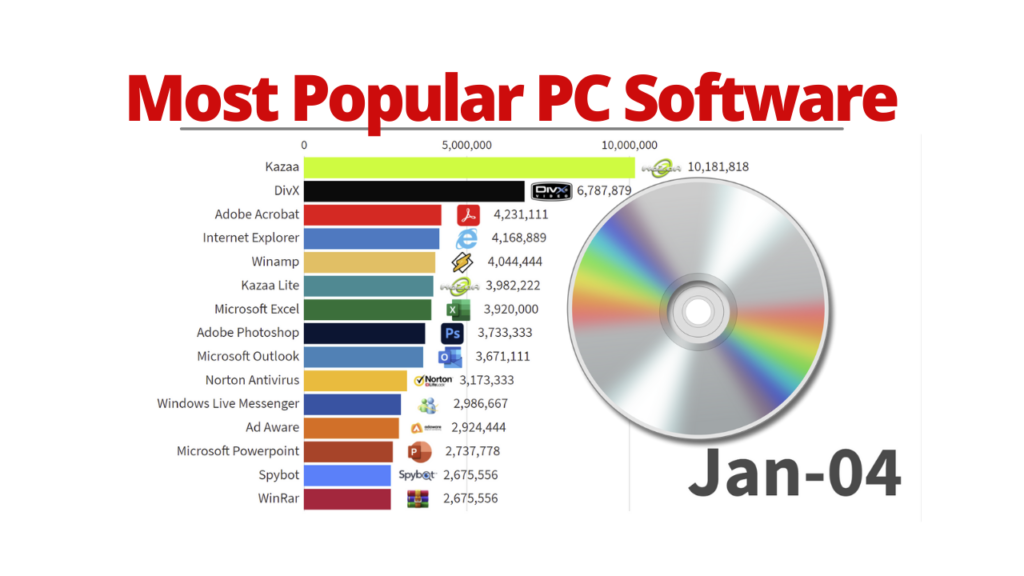
This image is property of statisticsanddata.org.
Antivirus Software
Importance of Antivirus Software
As computers are increasingly connected to the internet and networks, the importance of antivirus software cannot be overstated. Antivirus software plays a crucial role in protecting computers from malicious software, commonly known as malware. Malware can include viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and other forms of malicious code that can cause significant harm to a computer system. Antivirus software helps detect, prevent, and remove malware, ensuring the security and integrity of the computer and its data.
How Antivirus Software Works
Antivirus software works by employing a variety of techniques to analyze files, programs, and system activities to identify and neutralize potential threats. Some common methods used by antivirus software include:
-
Signature-based Detection: Antivirus software compares files and programs against a database of known malware signatures. If a file matches a known signature, it is flagged as malware and dealt with accordingly.
-
Heuristic Analysis: Antivirus software uses heuristics to identify suspicious behavior or characteristics that may indicate the presence of malware. This analysis helps catch emerging threats that do not have known signatures.
-
Behavior Monitoring: Antivirus software monitors the behavior of files and programs in real-time, detecting any unusual or malicious activity. This method is especially effective against new and previously unknown malware.
-
Real-time Scanning: Antivirus software continuously scans files and programs as they are accessed or executed, providing immediate protection against potential threats.
Features to Look for in Antivirus Software
When choosing antivirus software, it is essential to consider various features and capabilities to ensure optimal protection. Some key features to look for in antivirus software include:
-
Real-time Protection: Look for antivirus software that provides continuous, real-time scanning and protection to detect and block threats as they occur.
-
Malware Removal: Ensure that the software is capable of effectively removing malware from infected systems, including quarantining and deleting malicious files.
-
Automatic Updates: Regular updates are crucial to keeping the antivirus software’s database of malware signatures up to date, ensuring protection against the latest threats.
-
Firewall Integration: Some antivirus software includes an integrated firewall to provide additional protection against network-based threats and unauthorized access.
-
Email and Web Protection: Look for antivirus software that offers email scanning and web protection features to safeguard against malware delivered through these channels.
Popular Antivirus Software Programs
There are several reputable antivirus software programs available on the market, each with its strengths and features. Some popular antivirus software programs include:
-
Norton Antivirus: Norton is a well-known name in the antivirus market, offering comprehensive protection against malware, including real-time scanning, firewall integration, and online threat detection.
-
McAfee Antivirus: McAfee provides a range of security solutions, including antivirus software with features such as real-time protection, web and email scanning, and system optimization tools.
-
Avast Antivirus: Avast is a widely used antivirus program known for its robust protection, user-friendly interface, and extensive feature set. It offers real-time scanning, email and web protection, and behavior monitoring.
-
Bitdefender Antivirus: Bitdefender is a highly regarded antivirus software that offers advanced threat detection, password management, parental controls, and secure browsing features.
-
Kaspersky Antivirus: Kaspersky provides comprehensive protection against malware, with features such as real-time scanning, behavior monitoring, and network attack prevention.

This image is property of slideplayer.com.
Web Browser
Role of Web Browsers
Web browsers are essential software applications that allow users to access and navigate the World Wide Web. They act as a medium for retrieving and displaying web pages, enabling users to interact with websites, search for information, and access online services. Web browsers interpret HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code to render web content and provide a user-friendly interface for browsing the internet.
Key Considerations for Choosing a Web Browser
When selecting a web browser, there are several factors to consider to ensure a seamless browsing experience. Some key considerations include:
-
Speed and Performance: Look for a web browser that offers fast page loading, smooth scrolling, and efficient memory management for optimal performance.
-
Cross-platform Compatibility: Choose a web browser that is compatible with your operating system and devices to ensure a consistent browsing experience across different platforms.
-
Security: Consider the browser’s security features, such as built-in phishing and malware protection, privacy settings, and automatic updates to protect against online threats.
-
User Interface: The user interface of a web browser can greatly impact the browsing experience. Look for a browser with a clean, intuitive interface and customizable options to suit your preferences.
-
Extension and Add-on Support: Check the availability of extensions and add-ons that can enhance the functionality and features of the web browser.
Features and Extensions
Web browsers offer a wide range of features and extensions that can enhance the browsing experience and provide additional functionality. Some common features and extensions found in web browsers include:
-
Tabbed Browsing: Tabbed browsing enables users to have multiple web pages open in a single browser window, making it easier to navigate and switch between different sites.
-
Bookmarks and History: Web browsers allow users to save their favorite websites as bookmarks and access them easily. The browsing history feature keeps track of previously visited sites for quick reference.
-
Privacy and Security Settings: Web browsers provide options to enable or disable cookies, clear browsing data, and manage privacy settings to protect user information while browsing.
-
Password Management: Many web browsers offer built-in password managers that securely store login credentials and automatically fill them in when needed.
-
Ad-blockers: Extensions and add-ons can block unwanted advertisements and improve page loading times.
Examples of Popular Web Browsers
There are several popular web browsers available, each with its strengths and features. Some examples of widely used web browsers include:
-
Google Chrome: Chrome, developed by Google, is one of the most popular web browsers globally. It is known for its speed, stability, and extensive library of extensions.
-
Mozilla Firefox: Firefox is an open-source web browser known for its privacy features, customization options, and robust security measures.
-
Microsoft Edge: Edge is the default web browser for Windows 10 and offers a fast and secure browsing experience, with tight integration with other Microsoft services.
-
Safari: Safari is the default web browser for Apple devices, including Macs, iPhones, and iPads. It offers excellent performance, energy efficiency, and seamless integration with other Apple applications.
-
Opera: Opera is a feature-rich web browser that emphasizes speed, security, and customization options. It includes a built-in ad-blocker, VPN, and extensive sidebar extensions.

This image is property of shopnik.com.bd.
Productivity Software
Definition and Purpose
Productivity software, also known as office productivity software or office suites, refers to a collection of applications designed to enhance productivity and efficiency in various personal and professional tasks. This software enables users to create, edit, manage, and share documents, spreadsheets, presentations, and other types of digital content. Productivity software provides tools and features that streamline work processes, improve collaboration, and enhance the overall workflow.
Types of Productivity Software
There are several types of productivity software available, each catering to specific tasks and requirements. Some common types of productivity software include:
-
Word Processing Software: Word processing software allows users to create, edit, and format text-based documents such as letters, reports, and resumes. Popular word processing software includes Microsoft Word, Google Docs, and Apache OpenOffice Writer.
-
Spreadsheet Software: Spreadsheet software enables users to create and manipulate numerical data, perform calculations, and create visual representations of data through charts and graphs. Examples of spreadsheet software include Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, and LibreOffice Calc.
-
Presentation Software: Presentation software allows users to create and deliver visual presentations involving slides, images, videos, and animations. Popular presentation software includes Microsoft PowerPoint, Google Slides, and Apple Keynote.
-
Project Management Software: Project management software helps users plan, organize, and track tasks, resources, and timelines for projects. It facilitates collaboration, communication, and task delegation within teams. Examples of project management software include Trello, Asana, and Microsoft Project.
-
Note-taking Software: Note-taking software provides tools for capturing, organizing, and managing notes, ideas, and observations. It may include features such as cloud syncing, search capabilities, and integration with other applications. Examples of note-taking software include Evernote, OneNote, and Simplenote.
Examples of Popular Productivity Software Programs
There are several popular productivity software programs available, with each offering unique features and capabilities. Some well-known productivity software programs include:
-
Microsoft Office: Microsoft Office is one of the most widely used productivity software suites, offering applications such as Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook. It provides a comprehensive set of tools for creating and managing various types of digital content.
-
Google Workspace: Formerly known as G Suite, Google Workspace is a cloud-based productivity suite that includes applications such as Google Docs, Sheets, Slides, and Gmail. It facilitates real-time collaboration and seamless file sharing.
-
LibreOffice: LibreOffice is an open-source productivity suite that includes applications similar to Microsoft Office, such as Writer (word processing), Calc (spreadsheet), Impress (presentation), and Base (database). It provides compatibility with a wide range of file formats.
-
Apple iWork: iWork is a suite of productivity software developed by Apple for macOS and iOS. It includes applications such as Pages, Numbers, and Keynote, offering seamless integration with other Apple devices and services.
Benefits of Using Productivity Software
Using productivity software can have several benefits, both for individuals and organizations. Some key benefits of using productivity software include:
-
Efficiency and Time Savings: Productivity software streamlines tasks and automates processes, allowing users to accomplish work more quickly and efficiently. Features such as templates, formatting tools, and automation capabilities help save time and reduce manual effort.
-
Improved Collaboration: Productivity software enables real-time collaboration, allowing multiple users to work on the same document simultaneously. This enhances communication, fosters teamwork, and eliminates version control issues.
-
Enhanced Organization and Accessibility: Productivity software provides tools for organizing and managing digital content, making it easier to find, retrieve, and share files. Cloud-based solutions enable access to documents from anywhere, on any device.
-
Professional Presentation and Communication: With productivity software, users can create visually appealing documents, presentations, and reports, enhancing overall professionalism and communication effectiveness.
-
Cost Savings: Open-source productivity software, such as LibreOffice, provides cost-effective alternatives to proprietary software. Additionally, productivity software eliminates the need for paper-based documentation, reducing printing costs and environmental impact.
By leveraging the capabilities of productivity software, users can optimize their workflows, increase productivity, and achieve better outcomes in various personal and professional tasks.

This image is property of www.techyv.com.