Let’s break it down for you – SaaS, which stands for Software as a Service, is a game-changer in the world of technology. In a nutshell, SaaS refers to a cloud-based software delivery model where applications are hosted and managed by a third-party provider. This means that instead of installing software on your own computer or server, you can access it through the internet. It’s a convenient and flexible solution that allows businesses and individuals to access and use software applications without the hassle of installation, maintenance, and hardware costs. In this article, we’ll explore the ins and outs of SaaS, its benefits, and why it’s changing the way we work and live. So, grab a cup of coffee and get ready to dive into the world of SaaS!
This image is property of i0.wp.com.
What is SaaS?
Definition
SaaS, or Software-as-a-Service, is a model of delivering software applications over the internet. In this model, instead of purchasing and installing software on individual computers or servers, users access the software through a web browser. The software is hosted and maintained by the SaaS provider, who is responsible for the underlying infrastructure, security, and updates.
Characteristics
One of the key characteristics of SaaS is that it is subscription-based, meaning that users pay a recurring fee to access and use the software. This is a departure from traditional software models where customers would typically purchase a license for the software upfront. Additionally, SaaS applications are centrally hosted, allowing users to access the software from anywhere with an internet connection. This makes it ideal for remote teams or businesses with multiple locations.
Examples
There are many examples of SaaS applications available today. Some popular examples include Salesforce for customer relationship management (CRM), Slack for communication and collaboration, and Microsoft Office 365 for productivity tools such as Word, Excel, and PowerPoint. These examples highlight the versatility of SaaS, as it can be used across various industries and functions.
Advantages of SaaS
Cost-effective
One of the biggest advantages of SaaS is its cost-effectiveness. With traditional software, companies would typically have to purchase licenses for each user, which could be expensive, especially for larger organizations. SaaS, on the other hand, operates on a subscription model, allowing companies to pay for only the software and features they need. This eliminates the need for upfront investment and reduces the overall cost of ownership.
Scalability
Scalability is another significant advantage of SaaS. As businesses grow and their software needs increase, SaaS applications can easily scale to accommodate the growing user base or additional functionalities. SaaS providers typically offer different pricing tiers or plans, allowing businesses to upgrade or downgrade their subscription as needed. This flexibility ensures that companies can align their software costs with their business needs without having to invest in additional infrastructure or hardware.
Ease of use
SaaS applications are designed with ease of use in mind. They typically have intuitive user interfaces and require little to no technical expertise to get started. This means that employees can quickly adopt and utilize the software without the need for extensive training or support. Additionally, SaaS providers often offer customer support and regular updates, ensuring that users have access to the latest features and enhancements.
This image is property of www.tekrevol.com.
Disadvantages of SaaS
Dependency on Internet
One of the main disadvantages of SaaS is its dependency on internet connectivity. Since the software is accessed through a web browser, a stable and reliable internet connection is required for users to access and use the application. This can be problematic in areas with limited or unreliable internet access or during network outages. Companies must consider the potential impact of downtime or connectivity issues when relying on SaaS applications for critical business operations.
Limited customization
Another drawback of SaaS is the limited customization options available. Unlike traditional software that can be tailored to specific business needs, SaaS applications are generally designed to be used by a wide range of customers. This means that customization options may be limited, and companies may need to adapt their processes to fit within the constraints of the software. While customization can often be achieved through configuration settings, extensive modifications may not be possible.
Security concerns
Security is a significant concern when it comes to SaaS. Since the software and data are hosted by the SaaS provider, companies must trust that their data will be securely stored and protected against unauthorized access. It is crucial to thoroughly evaluate the security measures implemented by the SaaS provider, including data encryption, user authentication, and compliance with industry regulations. Additionally, companies must consider the potential risks of data breaches or service disruptions when choosing a SaaS solution.
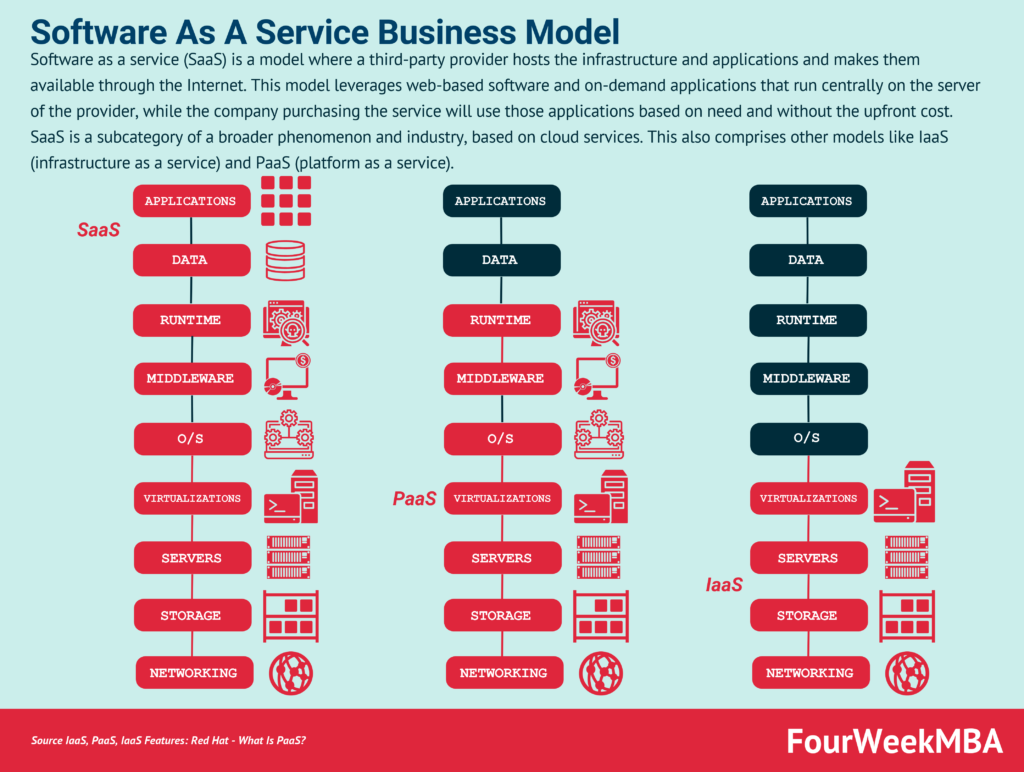
Working Principle of SaaS
Cloud Computing
SaaS relies on cloud computing technology, which involves the use of remote servers hosted on the internet to store, manage, and process data. These servers, often referred to as the cloud, serve as the infrastructure for delivering software applications to users over the internet. Cloud computing allows SaaS providers to scale their resources as needed to meet customer demands, ensuring reliable access to the software.
Subscription Model
The subscription model is at the core of SaaS. Instead of purchasing a license for the software upfront, users pay a recurring fee to access and use the software. This subscription fee typically includes maintenance, support, and updates. The subscription model allows companies to budget for software expenses on an ongoing basis, rather than making a significant upfront investment.
Multi-Tenancy
Multi-tenancy is a key concept in SaaS architecture. It refers to the ability of a single instance of the software to serve multiple customers, or tenants, simultaneously. Each tenant is isolated from the others, ensuring data privacy and security. Multi-tenancy allows SaaS providers to efficiently manage their resources and deliver cost-effective solutions to their customers.

This image is property of i0.wp.com.
Use Cases of SaaS
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
One of the most common use cases for SaaS is in customer relationship management (CRM). SaaS CRM applications allow businesses to manage customer interactions, track leads, and streamline sales and marketing processes. These applications often come with features such as contact management, opportunity tracking, and reporting, enabling companies to improve customer engagement and drive sales growth.
Human Resources (HR) Management
SaaS also offers significant benefits in the field of human resources (HR) management. SaaS HR applications provide companies with a centralized platform for managing various HR processes, including employee onboarding, benefits administration, time and attendance tracking, and performance management. These applications streamline HR operations, improve data accuracy, and enhance employee self-service capabilities.
Project Management
SaaS project management applications are widely used to facilitate collaboration and coordination among team members working on projects. These applications often include features such as task management, document sharing, Gantt charts, and project dashboards. With real-time access to project information, teams can effectively track progress, manage tasks, and communicate with stakeholders, leading to improved project outcomes.
SaaS vs. Traditional Software
Ownership
One of the key differences between SaaS and traditional software is ownership. With traditional software, companies typically own a perpetual license that allows them to use the software indefinitely. In contrast, SaaS operates under a subscription model, where companies do not own the software but instead pay for ongoing access to it. While traditional software offers the advantage of ownership, SaaS provides the benefit of continuous updates and support.
Upfront Costs
Another notable difference is the upfront costs associated with each model. Traditional software often requires a significant upfront investment in software licenses, hardware, and infrastructure. In contrast, SaaS eliminates the need for upfront costs, as companies only pay for the software on a recurring basis. This makes SaaS a more cost-effective option for businesses looking to minimize their initial investment and align their software expenses with their usage.
Updates and Maintenance
In terms of updates and maintenance, SaaS provides a more seamless experience compared to traditional software. SaaS applications are typically updated automatically by the provider, ensuring that users have access to the latest features and enhancements without having to go through the process of manual upgrades. Additionally, maintenance and support are often included as part of the subscription fee, reducing the burden on IT teams and allowing users to focus on the core activities of their business.
This image is property of i0.wp.com.
Key Players in the SaaS Space
Salesforce
Salesforce is one of the pioneering companies in the SaaS industry and is a leader in the CRM space. Its flagship product, Salesforce CRM, offers a comprehensive set of features for managing customer relationships, sales processes, and marketing campaigns. Salesforce has expanded its product portfolio to include solutions for customer service, e-commerce, and analytics, making it a dominant player in the SaaS market.
Microsoft 365
Microsoft 365, previously known as Office 365, is a suite of SaaS applications developed by Microsoft. It includes popular productivity tools such as Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook, as well as collaboration tools like Teams and SharePoint. Microsoft 365 provides businesses with a secure and integrated environment for communication, document collaboration, and content management.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a leading cloud computing platform that offers a wide range of SaaS solutions. In addition to providing infrastructure for hosting SaaS applications, AWS offers its own suite of SaaS products. Some notable examples include Amazon S3 for scalable storage, Amazon RDS for managed databases, and Amazon Redshift for data warehousing. AWS’s extensive offering makes it a key player in the SaaS market.
Security in SaaS
Data Encryption
Data encryption is a crucial security measure in SaaS applications. SaaS providers should employ strong encryption algorithms to protect data both at rest and in transit. This ensures that sensitive information remains secure from unauthorized access or interception. Companies should verify that their chosen SaaS provider has implemented robust encryption standards and practices to safeguard their data.
User Authentication
User authentication is another critical security aspect in SaaS. Strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, should be in place to verify the identity of users accessing the application. This helps prevent unauthorized users from gaining access to sensitive data or performing malicious activities within the software. It is essential for companies to evaluate the authentication methods implemented by the SaaS provider to ensure the highest level of security for their users.
Compliance
Compliance with industry regulations and standards is vital when it comes to SaaS security. Depending on the industry or the nature of the data being stored and processed, companies may have specific compliance requirements. SaaS providers should be transparent about their compliance certifications and offer assurances that their systems adhere to relevant regulations. This includes compliance with standards such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for data protection and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for healthcare data.

This image is property of www.selecthub.com.
Future Trends of SaaS
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
Artificial Intelligence (AI) integration is expected to play a significant role in the future of SaaS. AI technologies, such as machine learning and natural language processing, can enhance SaaS applications by providing intelligent insights, automation, and personalized experiences. SaaS providers are increasingly incorporating AI capabilities into their offerings to improve efficiency, productivity, and user satisfaction.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The Internet of Things (IoT) is another area that holds great potential for SaaS. By integrating with IoT devices, SaaS applications can gather real-time data from connected devices and enable intelligent automation and decision-making. This opens up opportunities for industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics to leverage SaaS solutions to optimize processes and improve operational efficiency.
Increased Industry-Specific Solutions
As SaaS continues to mature, there will likely be a rise in industry-specific solutions tailored to the unique needs of various sectors. SaaS providers will develop specialized applications and features that address specific challenges and requirements in industries such as healthcare, finance, and retail. This industry-specific approach will enable businesses to leverage SaaS solutions that are aligned with their specific workflows and compliance needs.
Conclusion
SaaS, or Software-as-a-Service, has revolutionized the way businesses access and use software applications. With its cost-effectiveness, scalability, and ease of use, SaaS has become a popular choice for organizations of all sizes and industries. While there are potential disadvantages, such as dependency on internet connectivity and limited customization, the benefits of SaaS outweigh these drawbacks for most companies. As the SaaS market continues to evolve, industry trends such as AI integration, IoT integration, and increased industry-specific solutions will shape the future of SaaS, providing businesses with even more value and innovation.