So you’ve heard the term “SaaS operating model” thrown around, but what exactly does it mean? Well, simply put, a SaaS operating model refers to the structure and processes that a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) company follows to deliver its products and services. It encompasses everything from how the company develops and maintains its software, to how it supports and interacts with its customers. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what a SaaS operating model entails and why it’s crucial for the success of SaaS businesses.
Definition of a SaaS Operating Model
Overview of SaaS
Before diving into what a SaaS operating model is, let’s first understand what SaaS stands for. SaaS is the acronym for Software as a Service, which is a cloud computing model where software is delivered over the internet. Instead of downloading and installing software on your computer, you can access it through a web browser. This software-as-a-service model is becoming increasingly popular as it offers numerous benefits to businesses and individuals.
Understanding the Operating Model
Now that we have a general understanding of SaaS, let’s examine what a SaaS operating model entails. A SaaS operating model is a framework that outlines the structure and processes involved in delivering and managing a SaaS product or service. It defines how the software is developed, deployed, and maintained to ensure the utmost efficiency and reliability.
Benefits of a SaaS Operating Model
Cost Savings
One of the most significant advantages of a SaaS operating model is cost savings. With traditional software, you would need to purchase licenses for each user, install and maintain the software on your own servers, and regularly update it. This can be costly in terms of upfront expenses and ongoing maintenance. In contrast, a SaaS operating model eliminates the need for upfront investments in hardware and software licenses. Instead, you pay a subscription fee based on the number of users, which can significantly reduce your IT expenses.
Scalability
Another benefit of a SaaS operating model is scalability. Traditional software often requires additional resources and infrastructure when your business grows or when you experience sudden spikes in demand. With a SaaS operating model, scaling up or down is much simpler. The service provider takes care of the infrastructure, ensuring that the software can handle increased usage without causing disruptions or compromising performance.
Flexibility and Customization
A SaaS operating model also offers flexibility and customization options. Many SaaS providers allow you to tailor the software to meet your specific needs. You can choose different features, add-ons, or integrations that align with your business requirements. This flexibility ensures that the software adapts to your unique workflows and processes, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
Automatic Updates and Maintenance
Gone are the days of manually updating software or worrying about outdated versions. With a SaaS operating model, the service provider takes care of all updates and maintenance tasks. This means you always have access to the latest features and security patches without any effort on your part. Automatic updates also help ensure compatibility with other software or devices, making the overall user experience seamless.
Accessibility and Collaboration
A key advantage of a SaaS operating model is the accessibility and collaboration it enables. Since the software is hosted on the cloud, you can access it from anywhere with an internet connection. This is particularly beneficial for remote teams or businesses with multiple locations. It promotes collaboration as team members can work on the same documents or projects in real-time, regardless of their physical location.
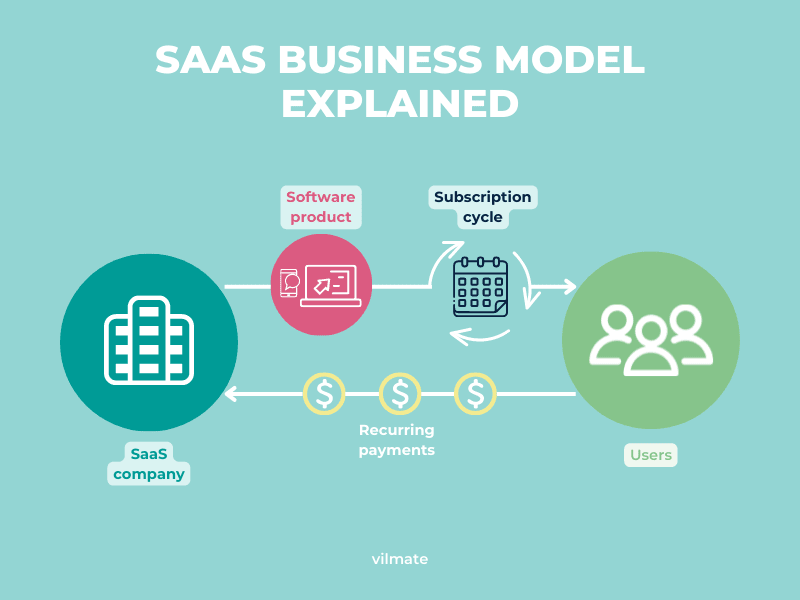
This image is property of vilmate.com.
Key Components of a SaaS Operating Model
User Interface and Experience
The user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) are crucial components of a SaaS operating model. A well-designed UI ensures that the software is intuitive and easy to navigate, while a seamless UX enhances user satisfaction and productivity. SaaS providers invest significant effort in creating visually appealing interfaces that are user-friendly and provide a pleasant experience.
Data Management
Effective data management is vital in a SaaS operating model. This includes data storage, retrieval, and security. SaaS providers handle the storage of user data on their servers, ensuring that it is safe and easily accessible. They employ robust backup systems and disaster recovery plans to protect against data loss. Additionally, data management in a SaaS operating model often involves features such as data analytics and reporting, empowering businesses to make data-driven decisions.
Security and Compliance
Security and compliance play a crucial role in a SaaS operating model. SaaS providers are responsible for implementing strong security measures to safeguard user data from unauthorized access or breaches. This includes encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits. Compliance with relevant industry regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, is also essential for businesses operating in specific sectors.
Infrastructure and Backend
The infrastructure and backend components of a SaaS operating model refer to the underlying technology and architecture that supports the software. SaaS providers invest in robust infrastructure to ensure reliable and high-performance service delivery. This involves data centers, servers, networks, and other hardware components that enable seamless software operation.
Integration and API
Integration capabilities are vital in a SaaS operating model. Businesses often rely on multiple software and systems to perform different functions. SaaS providers offer APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow seamless integration with other software applications. This enables data flow and interoperability between different tools, enhancing efficiency and streamlining workflows.
Analytics and Reporting
Analytics and reporting functionalities are increasingly becoming standard in SaaS operating models. Businesses need insights into their data to make informed decisions. SaaS providers often incorporate analytics and reporting tools that allow users to visualize data, generate reports, and gain valuable insights. This empowers businesses with the ability to track performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
Implementing a SaaS Operating Model
Planning and Strategy
Implementing a SaaS operating model involves careful planning and strategy. It is important to evaluate your business needs, identify the processes and areas that could benefit from a SaaS solution, and set clear objectives for the implementation. This includes defining the scope of the project, establishing timelines, and allocating resources.
Choosing the Right SaaS Provider
Selecting the right SaaS provider is critical for a successful implementation. Consider factors such as the provider’s reputation, experience, security measures, support services, and scalability. It is essential to thoroughly evaluate potential providers and choose one that aligns with your business goals and technical requirements.
Data Migration and Integration
Migrating your data to the new SaaS solution and integrating it with existing systems can be a complex process. Proper planning, data cleansing, and mapping are essential to ensure a smooth transition. Work closely with your SaaS provider to develop a migration strategy and verify that the data is transferred accurately and securely.
Testing and Training
Before fully adopting the SaaS operating model, comprehensive testing and user training are crucial. Test the software extensively to ensure that it meets your functional and performance requirements. Provide adequate training and support to your team members to ensure they can effectively utilize the software and maximize its benefits.
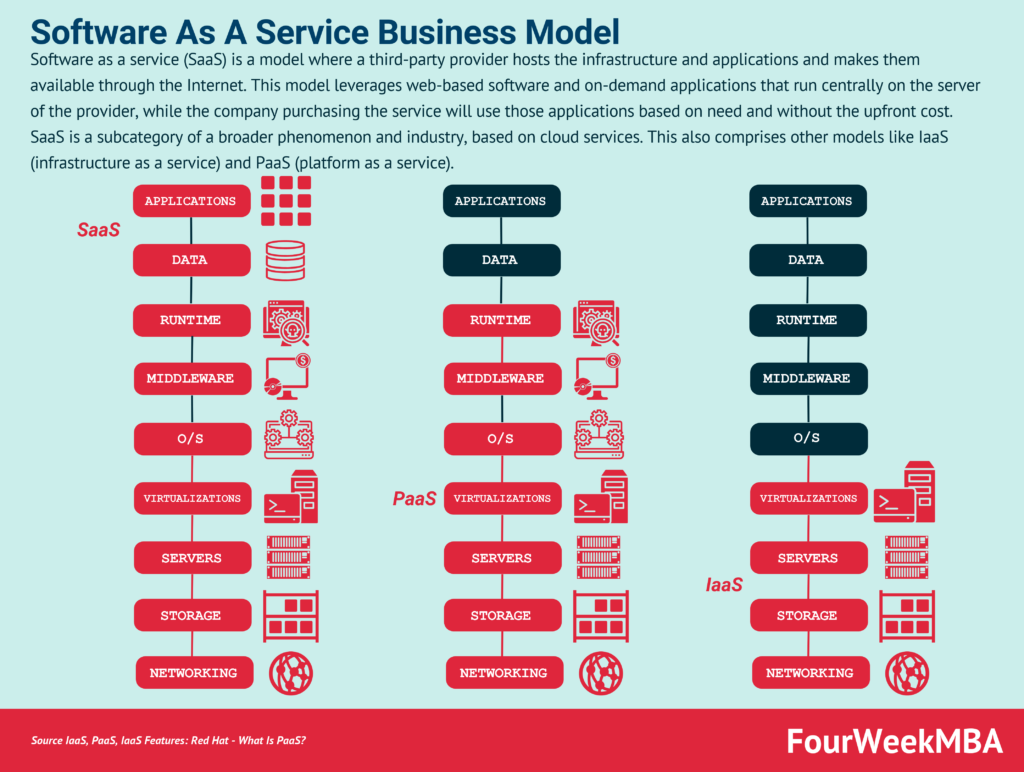
This image is property of fourweekmba.com.
Challenges of a SaaS Operating Model
Data Security and Privacy
While SaaS providers invest significant resources in ensuring data security, concerns about data breaches and unauthorized access are still valid. It is crucial to thoroughly understand the security measures implemented by your chosen SaaS provider and verify that they align with your organization’s security requirements. Additionally, proper data handling and compliance with privacy regulations should be considered to protect sensitive data.
Vendor Lock-In
Vendor lock-in is a potential challenge with a SaaS operating model. Once you have invested time and resources in migrating to a specific SaaS solution, it can be challenging to switch to another provider or revert to a different software model. It is important to carefully evaluate and consider factors such as contract terms, scalability, and portability before committing to a specific SaaS provider.
Customization and Integration Limitations
While many SaaS solutions offer flexibility and customization options, there may be limitations. Some SaaS providers have predefined features and configurations, which may not fully align with your specific requirements. It is essential to assess the extent of customization and integration capabilities provided by the SaaS solution to ensure it meets your business needs.
Reliance on Internet Connectivity
One potential challenge of a SaaS operating model is the reliance on internet connectivity. Since the software is accessed over the internet, any disruptions or slow internet speeds can hamper productivity. It is essential to have a reliable and robust internet connection to ensure uninterrupted access to the SaaS solution.
Best Practices for Managing a SaaS Operating Model
Continuous Monitoring and Performance Management
To ensure smooth operation of the SaaS operating model, continuous monitoring and performance management are essential. Regularly monitor the software’s performance, analyze metrics, and address any potential issues promptly. This includes monitoring response times, server uptime, and user satisfaction. Proactive management and optimization can enhance the overall user experience.
Regular Data Backups and Disaster Recovery
Data backup and disaster recovery are critical aspects of managing a SaaS operating model. Ensure that your SaaS provider has robust backup systems in place to protect against data loss. Regularly test the backup systems to verify their effectiveness. Additionally, develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan to minimize downtime and data loss in the event of unforeseen circumstances.
Contract Management and Service Level Agreements
Effective contract management and service level agreements (SLAs) are important for managing a SaaS operating model. Carefully review and understand the terms and conditions of your service contract. Pay attention to factors such as uptime guarantees, response times for support requests, and data protection policies. Regularly review and renegotiate contracts to ensure they align with your evolving business needs.
User Adoption and Training
To maximize the benefits of a SaaS operating model, focus on user adoption and training. Provide comprehensive training to your team members to ensure they have the necessary skills to fully utilize the software’s capabilities. Encourage user feedback and address any concerns or issues promptly. Promoting a culture of continuous learning and adoption can enhance user satisfaction and productivity.
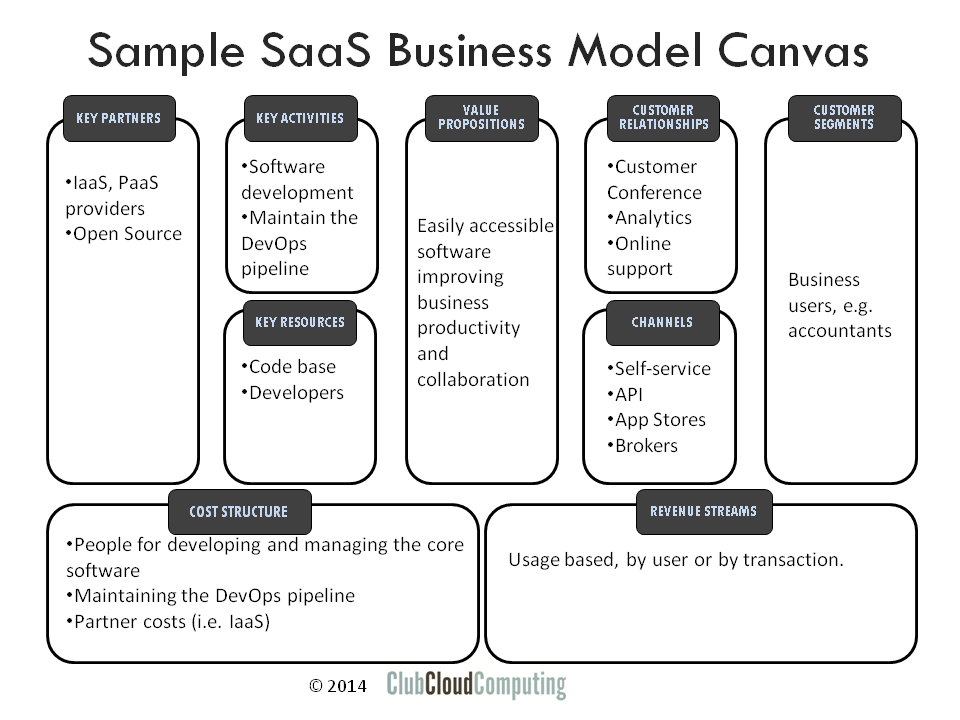
This image is property of www.clubcloudcomputing.com.
Examples of Successful SaaS Operating Models
Salesforce
Salesforce is a prime example of a successful SaaS operating model. It offers a comprehensive suite of cloud-based CRM (Customer Relationship Management) tools that enable businesses to manage customer data, track sales pipelines, and enhance customer relationships. Salesforce has gained widespread adoption due to its scalability, flexibility, and robust features tailored for various industries.
Microsoft Office 365
Microsoft Office 365 is another example of a successful SaaS operating model. It provides a suite of productivity tools, including Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook, delivered through the cloud. With Office 365, users can access their files and collaborate in real-time, regardless of the device or location. It offers seamless integration with other Microsoft products and services, making it a popular choice for businesses of all sizes.
Adobe Creative Cloud
Adobe Creative Cloud is a widely used SaaS operating model in the creative industry. It offers a range of applications for graphic design, photography, video editing, and web development. Creative professionals can access these applications through a subscription model, providing the latest versions and updates. Adobe Creative Cloud streamlines workflows, facilitates collaboration, and empowers users to bring their creative visions to life.
Future Trends in SaaS Operating Models
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) integration are expected to play a significant role in the future of SaaS operating models. AI and ML technologies can enhance automation, improve predictive capabilities, and deliver more personalized experiences for users. SaaS providers are increasingly incorporating AI and ML features into their software, enabling businesses to gain valuable insights and optimize their operations.
Internet of Things Connectivity
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to grow, SaaS operating models will likely incorporate IoT connectivity. IoT devices create vast amounts of data, which can be leveraged to drive actionable insights and improve decision-making. SaaS solutions that can seamlessly integrate with IoT devices and leverage the data they generate will become essential in various industries, from healthcare to manufacturing.
Edge Computing
Edge computing refers to processing and analyzing data closer to the source, rather than relying solely on central servers or the cloud. This approach reduces latency and enhances real-time decision-making capabilities. SaaS operating models are expected to embrace edge computing, enabling faster and more efficient data processing for applications such as autonomous vehicles, smart homes, and industrial IoT.
Subscription-Based Pricing Models
Subscription-based pricing models have become increasingly popular in SaaS operating models. Instead of large upfront costs, businesses pay a recurring subscription fee for access to the software. This allows businesses to allocate their budget more effectively and easily scale their software usage based on their needs. Subscription-based pricing models are likely to continue gaining traction, offering flexibility and affordability to users.
This image is property of jelvix.com.
Conclusion
A SaaS operating model offers numerous benefits to businesses, including cost savings, scalability, flexibility, and easy access to the latest software updates. Key components of a SaaS operating model include user interface and experience, data management, security and compliance, infrastructure and backend, integration and API, and analytics and reporting. Implementing a SaaS operating model requires careful planning, choosing the right provider, data migration and integration, and thorough testing and training. Challenges such as data security, vendor lock-in, and customization limitations should be considered and managed. Best practices for managing a SaaS operating model include continuous monitoring, data backups, contract management, and user adoption. Successful examples of SaaS operating models include Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, and Adobe Creative Cloud. Future trends in SaaS operating models include AI and ML integration, IoT connectivity, edge computing, and subscription-based pricing models. Embracing a SaaS operating model can empower businesses to enhance efficiency, collaboration, and innovation in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape.
